Human behavior is a complex process that involves the interplay between thoughts, feelings, and behaviors. Each of these components can have a significant impact on the others. For example, our thoughts can influence our feelings and behaviors, while our behaviors can impact our thoughts and feelings. Our emotions can also play a critical role in shaping our thoughts and behaviors. In other words, the way you think and feel about something can affect what you do.
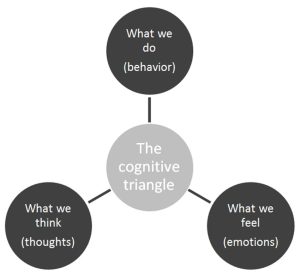
How does the cognitive triangle work?
One way that thoughts impact feelings and behaviors is through our cognitive processes. Our beliefs, values, and past experiences can all influence how we interpret events and situations. For example, if we have a negative belief about ourselves, we may interpret feedback from others in a negative way, which can lead to negative feelings and behaviors.
Behaviors also impact thoughts and feelings through a feedback loop. Our actions can influence our thoughts and feelings, which can, in turn, influence our behavior. For example, if we engage in behavior that makes us feel good, it can improve our mood and make us more likely to engage in similar behaviors in the future.
Feelings can also impact thoughts and behaviors. Our emotions can be a natural response to our thoughts or external stimuli, and they can influence our thoughts and behaviors in both positive and negative ways. For example, if we feel anxious, it can lead to negative thoughts and behaviors, such as avoidance or rumination.
Cognitive-behavioral therapy
Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is a model of emotion that is based on the idea that our thoughts, feelings, and behaviors are interconnected. CBT focuses on identifying and changing negative thought patterns and behaviors to improve our emotional well-being. CBT aims to help you identify and explore the ways your emotions and thoughts can affect your actions. Once you notice these patterns, you can begin learning how to change your behaviors and develop new coping strategies.
This approach involves several techniques, such as cognitive restructuring, behavioral activation, and relaxation techniques.
Cognitive restructuring involves identifying negative thought patterns and replacing them with more positive and realistic thoughts. For example, if we have a negative thought about a situation, we can challenge that thought by asking ourselves if it is accurate or helpful.
Behavioral activation involves identifying and engaging in activities that bring us pleasure and a sense of accomplishment. This can help improve our mood and reduce negative thoughts and behaviors.
Relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing or progressive muscle relaxation, can help reduce stress and improve our ability to cope with negative emotions.
How Does CBT work for Anger?
Anger is a common emotion that everyone experiences from time to time. However, when anger becomes intense and uncontrollable, it can harm our well-being and relationships. Anger management is the process of recognizing the signs of anger and learning how to control it healthily and productively. One key aspect of developing anger management habits is identifying triggers.
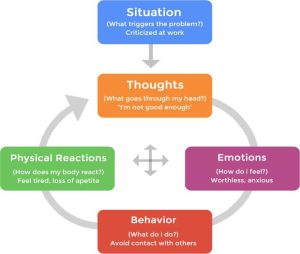
Triggers are situations or people that tend to set off feelings of anger. These triggers can be anything from traffic congestion to a difficult colleague at work. By identifying these triggers, individuals can prepare themselves to manage their responses when faced with them. For example, if a person knows that rush-hour traffic tends to make them angry, they may plan their commute to avoid the busiest times of the day.
Another important aspect of identifying triggers is recognizing the physical and emotional responses that occur when anger is triggered. This can include increased heart rate, tense muscles, and feelings of frustration or irritation. By understanding these physical and emotional cues, individuals can learn to recognize when they are becoming angry and take steps to calm down before the situation escalates.
One effective technique for managing anger is deep breathing. When anger is triggered, taking a few slow, deep breaths can help to calm the body and reduce feelings of anger. Other techniques for managing anger include mindfulness, physical activity, and talking to a trusted friend or therapist.
Developing anger management habits takes time and effort, but it can have a significant impact on overall well-being and relationships. By identifying triggers, recognizing physical and emotional responses, and learning effective techniques for managing anger, individuals can gain control over their emotions and improve their quality of life.
In conclusion, managing anger is an ongoing journey that requires consistent effort and practice. The Habitomic approach can be a helpful tool for developing new habits that support emotional well-being. By incorporating mini habits into your daily routine, such as deep breathing or mindfulness meditation, you can begin to retrain your brain and develop healthier patterns of thought and behavior. Habitomic can accompany you through this journey by providing personalized guidance and support, helping you to identify the habits that will be most effective for you. With time and practice, these habits can become second nature, allowing you to better manage your anger and improve your overall emotional well-being.

